
Privacy statement: Your privacy is very important to Us. Our company promises not to disclose your personal information to any external company with out your explicit permission.
Polytetrafluoroethylene (Poly tetra fluoroethylene), the English abbreviation of PTFE , commonly known as "Plastic King", the brand name is teflon. In China, due to the pronunciation, the trademark "Teflon" is also called Teflon, Teflon Dragon, Teflon, Teflon, Teflon, etc. are all transliterations of Teflon.
Polytetrafluoroethylene is known as the "King of Plastics." Roy Plunkett, the father of fluororesin, began researching substitutes for Freon at DuPont in the United States in 1936. They collected part of the tetrafluoroethylene and stored it in cylinders to prepare for the second They conducted the next experiment the next day, but when they opened the pressure reducing valve of the cylinder the next day, no gas escaped. They thought it was a gas leak, but when they weighed the cylinder, they found that the cylinder had not lost weight. They sawed open the cylinder and found a large amount of white powder, which was polytetrafluoroethylene.

Their research found that polytetrafluoroethylene has excellent properties and can be used in anti-melt sealing gaskets for atomic bombs, artillery shells, etc. Therefore, the U.S. military kept this technology secret during World War II. It was not until the end of World War II that it was declassified, and industrial production of PTFE was achieved in 1946.
1. Product name: PTFE
2. English name: Polytetrafluoroethylene
3. Alias
PTFE; Teflon; Teflon; teflon; Teflon; F4; King of plastics; Teflon (Japanese) [English abbreviation is
PTFE, the brand name is Teflon, and the Chinese translation is different in different places: Mainland China translates it as Teflon, Hong Kong translates it as Teflon, and Taiwan translates it as Teflon]
4. Molecular formula:
[CF2CF2]n
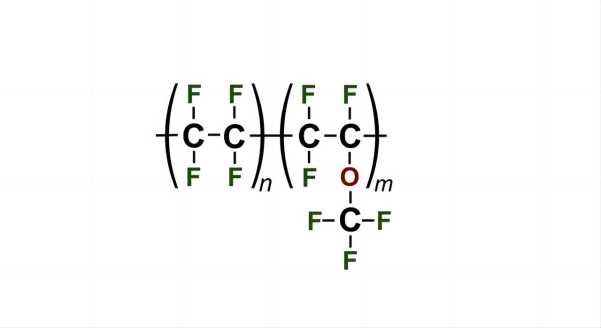
5. Production method
PTFE
Produced by free radical polymerization of tetrafluoroethylene. Industrial polymerization reactions are carried out with stirring in the presence of a large amount of water to disperse the heat of reaction and facilitate temperature control. Polymerization is generally carried out at 40 to 80°C and a pressure of 3 to 26 kgf/cm2. Inorganic persulfates and organic peroxides can be used as initiators, or a redox initiating system can be used. Each mole of tetrafluoroethylene releases heat of 171.38kJ during polymerization. Dispersion polymerization requires the addition of perfluorinated surfactants, such as perfluorooctanoic acid or its salts.
6. Application
Polytetrafluoroethylene [PTFE, F4] is one of the materials with the best corrosion resistance in the world today, so it is known as the "King of Plastics". It can be used in any kind of chemical media for a long time, and its production has solved many problems in my country's chemical industry, petroleum, pharmaceutical and other fields. PTFE seals, gaskets, and gaskets. PTFE seals, gaskets, and gaskets are molded from suspension polymerized PTFE resin. Compared with other plastics, PTFE has excellent chemical corrosion resistance and temperature resistance. It has been widely used as sealing material and filling material. It has a high degree of chemical stability and excellent resistance to chemical corrosion, such as resistance to strong acids, strong alkali, strong oxidants, etc. It has outstanding heat resistance, cold resistance and wear resistance. The long-term use temperature range is -200-+250℃. It has excellent electrical insulation and is not affected by temperature and frequency. In addition, it has the characteristics of non-stick, non-absorbent and non-burning. Suspension resin is generally formed and processed by molding and sintering. The resulting rods, plates or other profiles can be further processed by machining methods such as turning, drilling, and milling. The bar can then be turned and drawn into an oriented film.

7. Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) characteristics
1. Strength (high strength-to-weight ratio)
2. Chemically inert
3. Biological adaptability
4. High thermal resistance
5. High chemical resistance in harsh environments
6. Low flammability
7. Low friction coefficient
8. Low dielectric constant
9. Low water absorption
10.Good weathering properties
PTFE is a polymer of tetrafluoroethylene. The English abbreviation is PTFE. The trade name is "Teflon". Known as the "King of Plastics". The basic structure of polytetrafluoroethylene is - CF2 - CF2 - CF2 - CF2 - CF2 - CF2 - CF2 - CF2 - CF2 - CF2 -. Polytetrafluoroethylene is widely used in various applications that require resistance to acids, alkalis and organic solvents. It is not toxic to humans, but perfluorooctanoate (PFOA), one of the raw materials used in the production process, is considered to be potentially carcinogenic. The relative molecular weight of polytetrafluoroethylene is relatively large, ranging from hundreds of thousands to more than 10 million, and generally millions (the degree of polymerization is on the order of 104, while Polyethylene is only 103). Generally, the crystallinity is 90 to 95%, and the melting temperature is 327 to 342°C. The CF2 units in the polytetrafluoroethylene molecule are arranged in a zigzag shape. Since the radius of the fluorine atom is slightly larger than that of hydrogen, the adjacent CF2 units cannot be completely trans-cross-oriented, but form a spiral twisted chain, which is almost covered by the fluorine atoms. on the surface of the entire polymer chain. This molecular structure explains PTFE's various properties. When the temperature is lower than 19°C, a 13/6 helix is formed; at 19°C, a phase change occurs, and the molecules are slightly unraveled, forming a 15/7 helix.
8. Chemical properties
The chemical structure of polytetrafluoroethylene is formed by replacing all hydrogen atoms in polyethylene with fluorine atoms.
The F atoms in the PTFE molecule cover the C-C bonds, and the C-F bond energy is high and particularly stable. It is not corroded by any chemicals except alkali metals and elemental fluorine.
The F atom in the PTFE molecule is symmetrical, and the two elements in C-F are covalently combined. There are no free electrons in the molecule, and the entire molecule is neutral. PTFE has excellent dielectric properties because there are no gram bonds in the molecular structure of PTFE, so its crystallinity is very high. Because there is an inert fluorine-containing shell outside the PTFE molecules, it has outstanding non-stick properties and low friction coefficient.
1. Insulation: not affected by the environment and frequency, the volume resistance can reach 1018 ohm cm, the dielectric loss is small, and the breakdown voltage is high.
2. High and low temperature resistance: The effect on temperature does not change much, the temperature range is wide, and the usable temperature is -190~260℃.
3. Self-lubricating: It has the smallest friction coefficient among plastics and is an ideal oil-free lubricating material.
4. Surface non-stickiness: No known solid material can adhere to the surface. It is a solid material with the smallest surface energy.
5. Atmospheric aging resistance, radiation resistance and low permeability: the surface and performance remain unchanged after long-term exposure to the atmosphere.
6. Non-flammability: Oxygen limiting index is below 90.
7. Chemical corrosion resistance and weather resistance: Except for molten alkali metals, PTFE is almost not corroded by any chemical reagents. For example, when boiled in concentrated sulfuric acid, nitric acid, hydrochloric acid, or even aqua regia, its weight and performance remain unchanged. It is also almost insoluble in all solvents, and is only slightly soluble in all alkanes above 300°C (about 0.1g/100g). PTFE does not absorb moisture, is non-flammable, and is extremely stable to oxygen and ultraviolet rays, so it has excellent weather resistance.
Although the cleavage of carbon-carbon bonds and carbon-fluorine bonds in perfluorocarbons requires energy absorption of 346.94 and 484.88kJ/mol respectively, the depolymerization of polytetrafluoroethylene to generate 1 mol of tetrafluoroethylene requires only 171.38kJ of energy. Therefore, during high-temperature cracking, polytetrafluoroethylene is mainly depolymerized into tetrafluoroethylene. The weight loss rates (%) of polytetrafluoroethylene at 260, 370 and 420°C are 1×10-4, 4×10-3 and 9×10-2 per hour respectively. It can be seen that PTFE can be used for a long time at 260℃. Since highly toxic by-products such as fluorophosgene and perfluoroisobutylene are also produced during high-temperature cracking, special attention must be paid to safety protection and to prevent polytetrafluoroethylene from coming into contact with open flames.
It does not melt at a temperature of 250°C and does not become brittle at an ultra-low temperature of -260°C. PTFE is extremely smooth, even ice cannot compare with it; its insulation properties are particularly good, a film as thick as newspaper is enough to withstand high voltage of 1500V.

9. Physical properties
PTFE is mechanically soft. Has very low surface energy.
Polytetrafluoroethylene (F4, PTFE) has a series of excellent performance properties: high temperature resistance - long-term use temperature of 200~260 degrees, low temperature resistance - still soft at -100 degrees; corrosion resistance - resistant to aqua regia and all organic solvents; Weather resistance - the best aging life in plastics; high lubrication - has the smallest friction coefficient in plastics (0.04); non-sticky - has the smallest surface tension in solid materials without adhering to anything; non-toxic - has physiological inertness ;Excellent electrical properties, ideal C-class insulation material. PTFE materials are widely used in important sectors such as national defense, atomic energy, petroleum, radio, electric machinery, and chemical industries.
10. Polytetrafluoroethylene products
PTFE rods, pipes, plates, turned plates. PTFE is a polymer of tetrafluoroethylene. The English abbreviation is PTFE. The structural formula is . It was discovered in the late 1930s and put into industrial production in the 1940s. Properties: The relative molecular weight of polytetrafluoroethylene is relatively large, ranging from hundreds of thousands to more than 10 million, and generally millions (the degree of polymerization is on the order of 104, while polyethylene is only 103). Generally, the crystallinity is 90 to 95%, and the melting temperature is 327 to 342°C. The CF2 units in the polytetrafluoroethylene molecule are arranged in a zigzag shape. Since the radius of the fluorine atom is slightly larger than that of hydrogen, the adjacent CF2 units cannot be completely trans-cross-oriented, but form a spiral twisted chain, which is almost covered by the fluorine atoms. on the surface of the entire polymer chain. This molecular structure explains PTFE's various properties. When the temperature is lower than 19°C, a 13/6 helix is formed; at 19°C, a phase change occurs, and the molecules are slightly unraveled, forming a 15/7 helix.
1. Mechanical properties: Its friction coefficient is extremely small, only 1/5 of polyethylene, which is an important feature of perfluorocarbon surface. And because the intermolecular force between fluorine and carbon chains is extremely low, PTFE is non-sticky.
2. Electrical properties: PTFE has low dielectric constant and dielectric loss in a wide frequency range, and has high breakdown voltage, volume resistivity and arc resistance.
3. Radiation resistance: The radiation resistance of polytetrafluoroethylene is poor (104 rad). It will be degraded after being exposed to high-energy radiation, and the electrical and mechanical properties of the polymer will be significantly reduced.
4. Polymerization: Polytetrafluoroethylene is produced by free radical polymerization of tetrafluoroethylene. Industrial polymerization reactions are carried out with stirring in the presence of a large amount of water to disperse the heat of reaction and facilitate temperature control. Polymerization is generally carried out at 40 to 80°C and a pressure of 3 to 26 kgf/cm2. Inorganic persulfates and organic peroxides can be used as initiators, or a redox initiating system can be used. Each mole of tetrafluoroethylene releases heat of 171.38kJ during polymerization. Dispersion polymerization requires the addition of perfluorinated surfactants, such as perfluorooctanoic acid or its salts.
5. Expansion coefficient (25~250℃): 10~12×10-5/℃. PTFE maintains excellent mechanical properties in a wide temperature range of -196 to 260°C. One of the characteristics of perfluorocarbon polymers is that they are not brittle at low temperatures.

11. Application fields
PTFE can be formed by compression or extrusion; it can also be made into an aqueous dispersion for coating, impregnation or fiber making. Polytetrafluoroethylene is widely used in industries such as atomic energy, national defense, aerospace, electronics, electrical, chemical industry, machinery, instruments, meters, construction, textiles, metal surface treatment, pharmaceuticals, medical care, textiles, food, metallurgy and smelting to withstand high and low temperatures. , corrosion-resistant materials, Insulation Materials, anti-stick coatings, etc., making it an irreplaceable product.
12. Polytetrafluoroethylene and its filled products
1. General materials: various rods, tubes, sheets, tapes, ropes, packing, and gaskets.
2. Anti-corrosion:
①. Pipes and accessories: pure PTFE pipe; PTFE-lined pipe; outer fiberglass reinforced plastic pipe; steel composite flange;
②. Chemical container lining: PTFE-lined kettle; PTFE-lined tank; PTFE-lined tower;
③.Heat exchanger;
④.Corrugated telescopic tube ;
⑤.Main components of valves and pumps;
⑥. Steel wire reinforced full pressure hose;
⑦. Filter material: The polytetrafluoroethylene membrane has a large number of pores after being stretched in both directions. It is a new material. By combining it with other fabrics, it can be made into a smoke solid-phase anti-corrosion filter bag or a good waterproof, breathable and windproof bag. Warm rain gear, sportswear, cold-proof clothing, special protective clothing and lightweight tents, compressed air for pharmaceuticals, sterile filtration of various solvents and filtration of high-purity gases in the electronics industry.
3. Sealing type:
①.Static sealing: sandwich gasket; seating belt; elastic sealing belt;
②.Dynamic seals (braided packing, ring seals): V-shaped sealing body - used for shafts, piston rods, valves; turbine pump internal seals; composite sealing rings of polytetrafluoroethylene and rubber; with bellows Telescopic mechanical seal.
4. Load-bearing category
①. Filled PTFE bearings, used in food, chemical, papermaking, and textile machinery;
②. Porous copper-impregnated fluoroplastic metal bearings can be used normally under high temperature, high pressure, dry friction and vacuum conditions;
③. Bearing lining of polytetrafluoroethylene fiber bearing made of composite fabric blended with polytetrafluoroethylene fiber and glass fiber or other fibers, used for low speed and high load;
④. Filling PTFE piston rings, guide rings, machine tool guide rails and bridge sliders;
5. Insulation type:
①. Class C insulation material for wires and cables;
②. Sheaths for stator and rotor water pipes and thermocouples of double water internally cooled turbine generators;
③.Microwave insulation materials for high-frequency and ultra-high-frequency communication equipment and radar;
④. Printed circuit substrates and insulation materials for motors and transformers (including gas transformers);
⑤. Insulation materials for air conditioners, electronic furnaces, various heaters and sulfur hexafluoride circuit breakers;
6. Anti-stick type:
①. The PTFE glass cloth coating on the hot roller of the sizing machine can avoid the roller sticking phenomenon caused by chemical slurry, greatly improving the production rate and gray cloth quality;
②.Microwave drying conveyor belts in the food industry - compared with conveyor belts made of other materials, they do not absorb microwave energy, so non-stick materials have the advantages of energy saving and cleaning;
③. Anti-adhesive material for heat sealing sleeves sealed in polyethylene bags;
④. Anti-stick coating - used for kitchen pots, bread baking molds, frozen food storage trays, electric iron bases, and copier rollers;
7. Temperature resistance:
①. The driving transmission device of microwave oven, such as the coupling and roller of microwave oven;
②. Temperature-resistant accessories for various refrigerators, air conditioners, oxygen generators, and compressors;
8. Other categories:
①. Human body substitutes arteries, veins, and cardiac membranes;
②.Endoscope, clamp catheter, trachea;
③. Other medical equipment such as tubes, bottles, filter cloths, etc.

LET'S GET IN TOUCH

Privacy statement: Your privacy is very important to Us. Our company promises not to disclose your personal information to any external company with out your explicit permission.

Fill in more information so that we can get in touch with you faster
Privacy statement: Your privacy is very important to Us. Our company promises not to disclose your personal information to any external company with out your explicit permission.